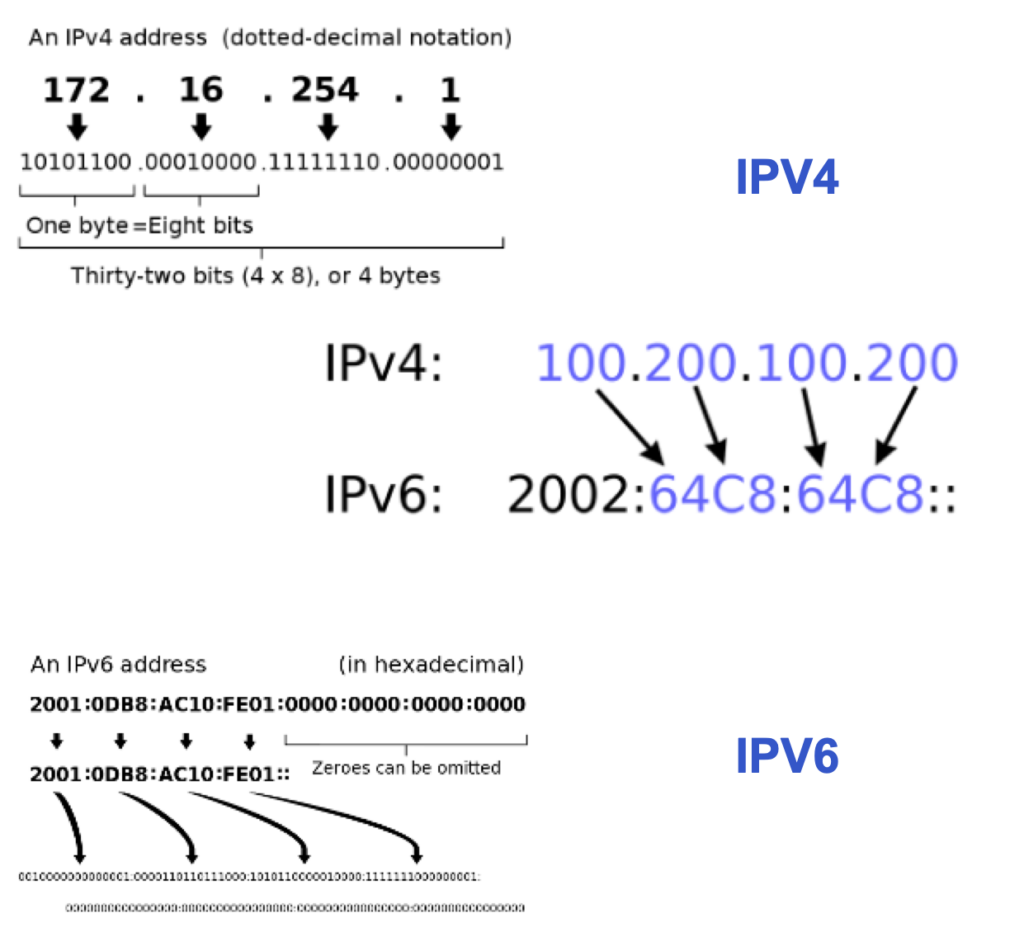
An Internet Protocol (IP) address, particularly an IPv4 network address, serves as a unique identifier enabling devices to communicate over the internet. This IPv4 address, part of an elaborate IPv4 addressing scheme, ensures data reaches its correct destination. For instance, an IPv4 address example like 192.168.1.1 demonstrates the structure defined by the IPv4 address scheme, which is pivotal for internet connectivity.
The question of “What is the IPv4?” pertains to understanding this critical component of internet architecture. Simply put, an IPv4 address is a 32-bit numerical label assigned to each device on a network, allowing for inter-device communication. As we delve deeper into “What is the IPv4 address”, it becomes clear that the design and allocation of these addresses are meticulously planned to optimize network efficiency and scalability.
The development of the IPv4 address scheme was a groundbreaking step in digital communication, yet the IPv4 addressing scheme faces significant challenges, notably IPv4 running out. This limitation, inherent in the finite nature of the IPv4 space, underscores the urgent need for migration to IPv6, which promises an almost limitless number of addresses.
IP addresses come in two main types: IPv4 and IPv6. ISPs typically offer both versions, and the choice depends on specific needs. IP addresses are hierarchical and divided into four or six parts called octets. Each section represents different information and plays a role in IP address allocation managed through routing protocols.
To ensure successful data transmission, internetworking protocols facilitate communication between IP networks. The process depends on network connectivity. Subnetting is used to divide networks into smaller subnetworks, optimizing IP address usage.
Overall, IP addresses are essential for Internet communication, and understanding their fundamentals is valuable for individuals working with computer networks and web programming.
A subnet, also known as a subnetwork, is a logical division of an IP network. Subnetting refers to the practice of splitting a network into multiple smaller networks. In the case of IPv4, a network can be identified by its subnet mask, which is a bitmask applied to an IP address using a bitwise and operation to determine the routing prefix.
For instance, consider the prefix 190.21.100.0/24, which has a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0. Subnet masks are typically represented in dot-decimal notation. Another example is 190.21.100.0/21, where 21 bits are allocated for the network prefix and the remaining 11 bits are reserved for host addressing in the IPv4 network.
When the routing prefixes of the source and destination addresses differ, traffic is routed between subnetworks through routers. Subnetting can improve routing efficiency and provide network management advantages, particularly when different entities within a larger organization have administrative control over specific subnetworks.
Subnets can be logically organized in a hierarchical architecture, enabling the partitioning of an organization’s network address space into a structured routing system.
IPv4 is the current protocol used for connecting to websites and servers, but it faces several challenges. One major issue is the depletion of available IPv4 addresses. An IP address is a numerical label assigned to devices to access network content. Due to the limited number of IPv4 addresses, we are running out of them. Fortunately, IPv6 offers a solution by providing a significantly larger pool of addresses, with the capacity to accommodate 2128 unique addresses for each individual on Earth.
IP, short for Internet Protocol, refers to a device’s specific location on a network. However, it can be confusing because there are two types of IP addresses: IPv4 and IPv6. IPv4 was created in 1981 and is commonly used for devices connected to home routers or office computer systems. On the other hand, IPv6 has been implemented more recently.
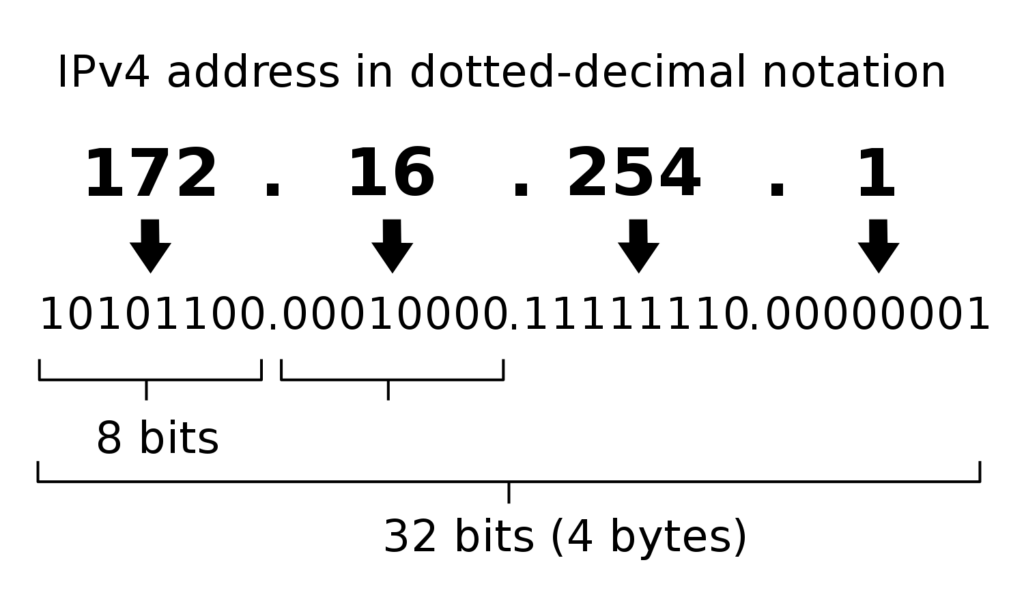
Despite their differences, both IPv4 and IPv6 are categorized as IP addresses. The main distinction between them is their size, with IPv4 being 32 bits long and IPv6 being 128 bits long. However, for consumers, the practical significance of this size difference is minimal. IP addresses typically appear as strings of numbers separated by dots. Nowadays, most computers support both IPv4 and IPv6 protocols, so the choice of which type to use when browsing online is often inconsequential.
An IPv4 address in a computer network is a series of four numbers separated by dots. Each number can range from 0 to 255, representing a unique identifier for a device on the network. For instance, if we have an IPv4 address like 212.168.0.0, the first number is 212, the second is 168, the third is 0, and the fourth is 255.

IPv6 is the latest version of the Internet Protocol and is designed to replace the current IPv4 protocol. It serves as a network layer protocol for transmitting data packets across multiple IP networks. IPv6 was developed to address the limitations and increasing demand for IP addresses in IPv4. Unlike IPv4, which uses 32-bit addresses, IPv6 utilizes a hierarchical structure with 128-bit addresses. Each bit in an IPv6 address represents a number from 0 to 256, and the address is divided into eight groups of four hexadecimal digits separated by colons. The implementation of IPv6 involves two layers: addressing, which determines the destination of packets, and routing, which determines the path for packet delivery. Every device connected to an IP network must have one or more unique IPv6 addresses associated with it.
IPv4 has a unique addressing system where each device connected to a network is assigned an individual IP address. However, the limitation of IPv4 is that it can only accommodate approximately 4.3 billion devices on a single network.
This limitation means that IPv4 addresses are running out, and Internet Service Providers (ISPs) are already facing shortages when providing IPv4 addresses to new customers. Consequently, there is a need to replace IPv4 with an alternative addressing scheme like IPv6 to overcome these limitations and ensure the availability of addresses for future devices.
Even if you do not own your IP address, you can still obtain one from specialized companies that sell them. Similar to how businesses ensure their physical locations are easily located on a map, they also want their IP addresses to be clearly communicated. Companies purchase large blocks of IPv4 addresses to allocate them among their branches and other sites, making it convenient for customers and potential partners to find them online. By assigning a unique IP number to each site, businesses ensure that their headquarters has a recognizable IP address readily available for visitors seeking their online information. Many different types of companies require a significant number of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, including internet service providers, hosting companies, cloud services, VPN services, various internet businesses, and banking/payment services.
There a lot of different companies which need to buy a lot of IPv4 and IPv6 addresses:
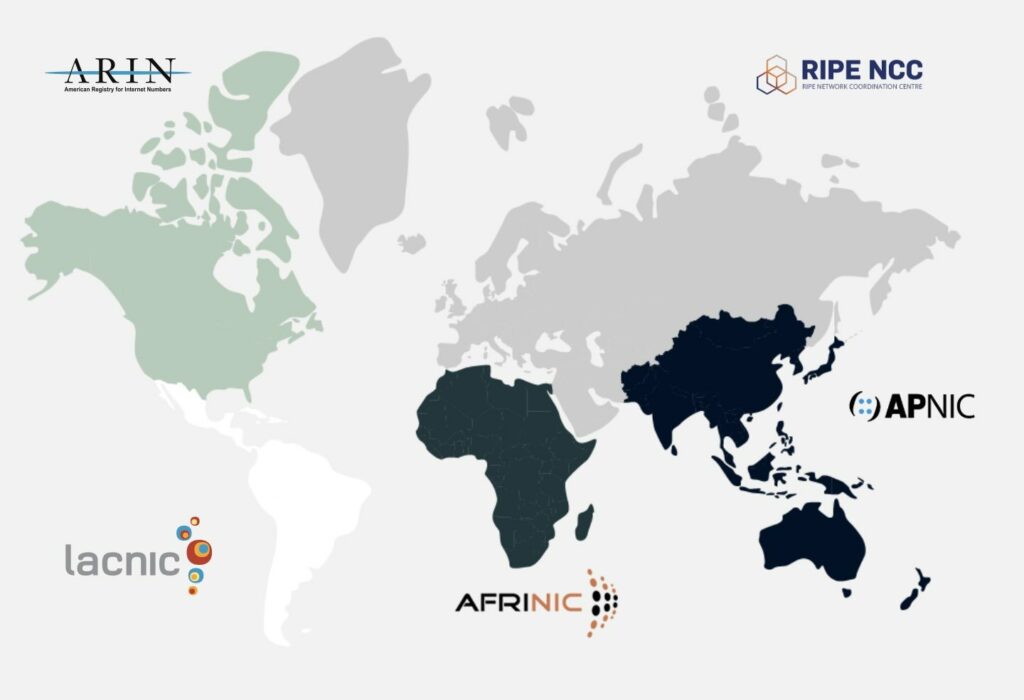
The majority of IP addresses are owned by Local Internet Registries (LIRs), which obtain IP space from Regional Internet Registries (RIRs) in blocks for private use within specific geographic regions. Each RIR is responsible for managing the availability of IP space, registering accounts for assignment within those spaces, and determining the allocation of IP blocks. The five RIRs are as follows:
Each RIR covers specific geographical regions and plays a vital role in the allocation and
management of IP addresses within their respective territories.
InterLIR: Monetizing, Renting, and Buying IPv4 Network Addresses
InterLIR offers a platform where companies can maximize the value of their unused IPv4 addresses by monetizing them. Additionally, we assist businesses in renting and purchasing IP addresses online at equitable prices. Take advantage of this opportunity by registering at https://portal.interlir.com and commencing your business journey with us.

Alexey Shkittin
CEO