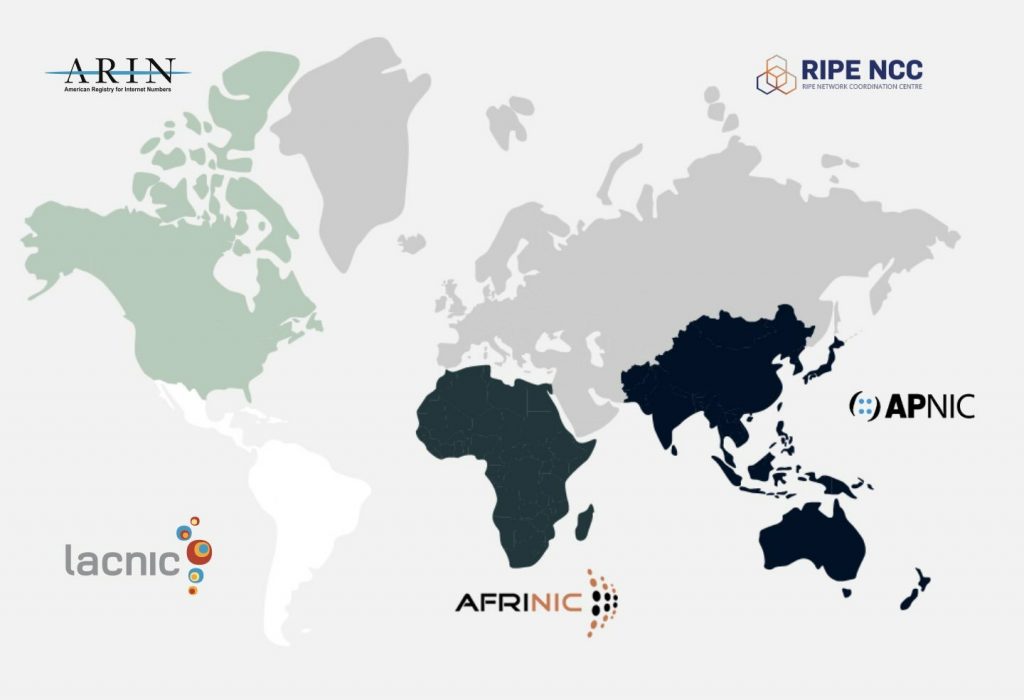
In today’s interconnected world, Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are crucial for the operation of networks. However, with the exhaustion of IPv4 addresses, organizations often find themselves needing to transfer IP resources within and between different regions. This article outlines the procedures and policies for transferring IP addresses between the American Registry for Internet Numbers (ARIN), Réseaux IP Européens Network Coordination Centre (RIPE NCC), and Asia-Pacific Network Information Centre (APNIC).

1. Understanding IP Transfer Policies
Each Regional Internet Registry (RIR) has specific policies governing the transfer of IP addresses. These policies ensure that transfers are conducted legally and responsibly, preserving the integrity and utility of IP address space.
2. Types of Transfers
Transfers can be categorized into intra-RIR (within the same RIR) and inter-RIR (between different RIRs). Intra-RIR transfers are generally more straightforward, subject to each RIR’s individual policies. Inter-RIR transfers, however, require compliance with policies of both the source and the recipient RIRs.
3. Transfer Requirements and Restrictions
ARIN:
- Requires the source to be the current rights holder and not involved in disputes.
- Imposes a 12-month restriction after receiving a transfer, allocation, or assignment from ARIN.
- Specifies that transferred IP addresses must be operationally used.
RIPE NCC:
- Allows the transfer of complete or partial IP address blocks to RIPE members or entities with a contractual relationship with a RIPE member.
- Enforces a 24-month hold period for newly received scarce resources.
- Requires updates in the RIPE Database to reflect the transfer.
APNIC:
- Demands that the source has the proper authority over the IP addresses.
- Stipulates that the recipient must demonstrate a legitimate need for the resources based on current APNIC policies.
- Provides an IPv4 Transfer Listing Service to facilitate finding potential transfer candidates.
4. Steps for Inter-RIR Transfers
- Initiation: The source organization initiates the transfer request through their respective RIR’s online platform.
- Approval: Both RIRs involved must evaluate and approve the transfer based on their policies.
- Documentation: Parties may need to provide legal and operational documents supporting the transfer.
- Completion: Upon approval and fulfillment of all conditions, the RIRs update their records to reflect the transfer.
5. Considerations for Effective IP Transfer
- Due Diligence: Verify the legitimacy and authority of the parties involved in the transfer.
- Compliance: Ensure that all transfer activities comply with the policies of the respective RIRs.
- Record-Keeping: Maintain accurate and updated records of the transfer in both RIR databases.
- Legal Advice: Consider obtaining legal counsel to navigate the complexities of international transfers.
Summary of Transfer Policies
| RIR | Transfer Types | Hold Period | Documentation Required | Policy Compliance |
| ARIN | Intra-RIR, Inter-RIR | 12 months | Officer Acknowledgement Letter | RSA, current policies |
| RIPE NCC | Intra-RIR, Inter-RIR | 24 months | Transfer reflected in RIPE Database | RIPE policies, usage rules |
| APNIC | Intra-RIR, Inter-RIR, Merger-Acquisition | None specified | Justification for need | APNIC policies, operational use |
Conclusion
Transferring IP addresses between ARIN, RIPE NCC, and APNIC involves navigating complex regulatory landscapes. By understanding the specific requirements and procedures of each RIR, organizations can effectively manage their IP resources and ensure seamless network operations across regions.